Actinic keratosis
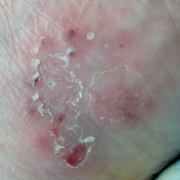 It may be possible to confuse Actinic keratosis with a spider bite. Actinic keratosis referred to as AK or solar keratosis is a premalignant condition of thick, scaly, or crusty patches of skin.
It may be possible to confuse Actinic keratosis with a spider bite. Actinic keratosis referred to as AK or solar keratosis is a premalignant condition of thick, scaly, or crusty patches of skin.
People who have fair skin are more likely to have this condition than others and it happens when fair skinned people are exposed to the sun. Some of these areas can lead to to squamous cell carcinoma and should be treated.
As skin is exposed to the sun for long periods of time, crusty, thick or scaly bumps may appear. The dry rough scaly (crusty) part of the bump starts out as flat scaly areas, and later grow into a tough, wart like area.
Actinic keratosis areas are usually between 2 to 6 millimeters, can be dark or light, tan, pink, red, a combination of all these, or the same pigment of one’s skin. It may appear on any sun-exposed area, such as the face, ears, neck, scalp, chest, back of hands, forearms, lips etc.
Actinic keratosis areas are classified as precancerous growths. If left untreated, approximately 1% of actinic keratoses develop into squamous cell carcinoma. Here are some examples of changes that could be cancer:
- Small, smooth, shiny, pale, or waxy lump (top left image)
- Firm, red lump (top right image)
- Sore or lump that bleeds or develops a crust or a scab (middle left image)
- Flat red spot that is rough, dry, or scaly and may become itchy or tender (middle right image)
- Red or brown patch that is rough and scaly (bottom image)


Sun damages warnings have to be taken seriously. However, it shouldn’t be forgotten that drugs and oils manufacturers have very much interest in frightening the consumers worldwide: the more they will be afraid of having their skin damaged by the sun, the more they will buy their products…
Amazing the damage the sun can do! I’ve seen this on my neighbor (I live in Florida).